Bogie stability and control strategy based on motor suspension
Article Text (Baidu Translation)
-
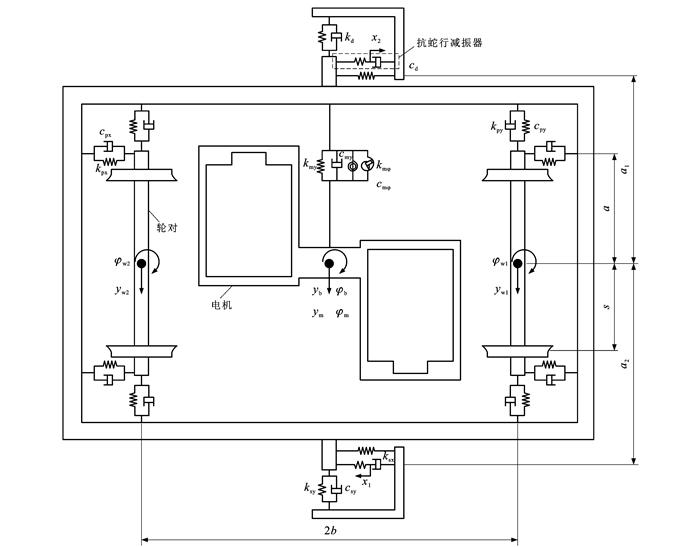
摘要: 实时调整架悬电机参数,以提高转向架的蛇行运动稳定性;建立了电机架悬转向架动力学模型,包含2个轮对、1个构架和2个电机,轮对和构架间考虑了一系悬挂装置,构架和车体间的二系悬挂装置考虑了空气弹簧和抗蛇行减振器,将2个电机考虑为一个整体并与构架弹性连接;基于高速转向架系统模型的最小阻尼比来寻找电机最优横移频率,分析了转向架参数对电机最优横移频率的影响,并针对该型转向架提出了一种能够提升蛇行运动稳定性的电机主动架悬反馈控制策略;通过开展电机主动架悬的高维车辆SIMPACK/SIMULINK联合仿真,对电机架悬控制策略进行了验证。研究结果表明:电机最优横移频率会随轮轨等效锥度的增大而增大,当轮轨等效锥度由0.3增大至0.6时,电机最优横移频率会由4.5 Hz增大到7.0 Hz;不同的等效锥度、电机质量和一系纵向刚度下,电机最优横移频率和转向架蛇行频率的差值均为1.0~1.5 Hz,因此,可通过检测转向架的蛇行频率再减去1.0~1.5 Hz获得电机最优横移频率,用电机和构架的相对位移和速度作为反馈信号,使电机能够实时获得最优架悬参数,成为理想的动力吸振器;高维数值仿真显示,电机主动架悬相比电机被动架悬可以使车轮磨耗后车辆的临界速度由370~380 km·h-1提高至500~510 km·h-1,并使构架横向加速度由2 m·s-2降低至1 m·s-2,说明提出的电机架悬控制策略可有效改善转向架的蛇行稳定性。Abstract: The motor suspension parameters were adjusted in real time to improve the hunting stability of vehicle bogie. A bogie dynamics model of motor suspension was established, including two wheelsets, one frame, and two motors. The primary suspension device was considered between wheelsets and frame, air springs and anti-yaw dampers were considered for the secondary suspension device between frame and car body, and the two motors were considered as a whole and elastically connected to the frame. Based on the minimum damping ratio of high-speed bogie system model, the optimal lateral frequency of motor was found. The influences of bogie parameters on the optimal lateral frequency of motor were analyzed, and an active motor suspension feedback control strategy was proposed for this type of bogie, so as to improve the hunting stability. Motor suspension control strategy was verified by carrying out a SIMPACK/SIMULINK joint simulation of high-dimensional vehicles with active motor suspension. Research results indicate that the optimal lateral frequency of motor increases with the increase of the equivalert conicity of wheel-rail, when the equivalent conicity of wheel-rail increases from 0.3 to 0.6, the optimal lateral frequency of motor increases from 4.5 Hz to 7.0 Hz. Under different equivalent conicities, motor masses, and primary longitudinal stiffnesses, the difference between the optimal lateral frequency of motor and the hunting frequency of the bogie is within the range of 1.0-1.5 Hz. Therefore, the optimal lateral frequency of motor can be obtained by detecting the hunting frequency of bogie and subtracting 1.0-1.5 Hz. The relative displacement and speed between motor and frame are used as feedback signals to obtain the optimal motor suspension parameters in real time, making it an ideal power absorber. High-dimensional numerical simulations show that compared with the passive motor suspension, the active motor suspension can increase the critical speed of vehicle with wheel worn from 370-380 km·h-1 to 500-510 km·h-1, and reduce the lateral acceleration of frame from 2 m·s-2 to 1 m·s-2, indicating that the proposed motor suspension control strategy can effectively improve the hunting stability of bogie.
-
Key words:
- vehicle engineering /
- bogie /
- stability /
- motor suspension parameter /
- control strategy /
- equivalent conicity
-
-
[1] 金鼎昌, 罗赟, 黄志辉. 牵引电动机悬挂方式对机车或动车动力学性能的影响[J]. 铁道学报, 1994(增1): 43-47. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDXB4S1.006.htmJIN Ding-chang, LUO Yun, HUANG Zhi-hui. Influence of traction motor suspension mode on dynamic performance of locomotive or motor train[J]. Journal of the China Railway Society, 1994(S1): 43-47. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDXB4S1.006.htm [2] 杨建伟, 郭宇轩, 王金海. 体悬式牵引电机悬挂参数对高速列车的振动特性影响[J]. 北京交通大学学报, 2023, 47(3): 122-129. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BFJT202303015.htmYANG Jian-wei, GUO Yu-xuan, WANG Jin-hai. Influence of suspension parameters of body suspension traction motor on vibration characteristics of high-speed train[J]. Journal of Beijing Jiaotong University, 2023, 47(3): 122-129. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BFJT202303015.htm [3] 罗赟, 金鼎昌. 架悬机车驱动装置悬挂参数规律的研究[J]. 中国铁道科学, 2007(4): 78-82. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGTK200704019.htmLUO Yun, JIN Ding-chang. Research on the rules of suspension parameters to driving equipments suspended in bogie frames[J]. China Railway Science, 2007(4): 78-82. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGTK200704019.htm [4] ALFI S, MAZZOLA L, BRUNI S. Effect of motor connection on the critical speed of high-speed railway vehicles[J]. Vehicle System Dynamics, 2008, 46(S1): 201-214. [5] 黄彩虹, 梁树林, 曾京, 等. 牵引电机架悬参数对动车转向架稳定性的影响[J]. 铁道车辆, 2014, 52(11): 1-5, 45. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDCL201411001.htmHUANG Cai-hong, LIANG Shu-lin, ZENG Jing, et al. Effect of the suspension parameter of traction motors on the stability of motor car bogies[J]. Rolling Stock, 2014, 52(11): 1-5, 45. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDCL201411001.htm [6] HUANG Cai-hong, ZENG Jing, LIANG Shu-lin. Influence of system parameters on the stability limit of the undisturbed motion of a motor bogie[J]. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part F: Journal of Rail and Rapid Transit, 2014, 228(5): 522-534. doi: 10.1177/0954409713488099 [7] 姚远, 张开林, 罗世辉, 等. 驱动系统弹性架悬对机车动力学性能影响机理[J]. 振动工程学报, 2012, 25(5): 481-487. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-4523.2012.05.001YAO Yuan, ZHANG Kai-lin, LUO Shi-hui, et al. The mechanism of dynamic effect of the driving system elastically mounted on the bogie frame of locomotive[J]. Journal of Vibration Engineering, 2012, 25(5): 481-487. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-4523.2012.05.001 [8] 姚远, 张开林, 张红军, 等. 机车驱动系统弹性架悬的机理与应用研究[J]. 铁道学报, 2013, 35(4): 23-29. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDXB201304005.htmYAO Yuan, ZHANG Kai-lin, ZHANG Hong-jun, et al. Mechanism of drive system elastic suspension and its application[J]. Journal of the China Railway Society, 2013, 35(4): 23-29. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDXB201304005.htm [9] 徐坤, 曾京, 黄彩虹, 等. 牵引电机架悬参数对动车转向架稳定性的影响[J]. 铁道学报, 2019, 41(8): 32-38. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDXB201908004.htmXU Kun, ZENG Jing, HUANG Cai-hong, et al. Influence of suspension parameters of traction motor on stability of high speed train bogie[J]. Journal of the China Railway Society, 2019, 41(8): 32-38. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDXB201908004.htm [10] 徐坤, 曾京, 黄彩虹, 等. 高速动车电机架悬参数对转向架动力学性能影响研究[J]. 振动与冲击, 2018, 37(20): 95-100, 108. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZDCJ201820015.htmXU Kun, ZENG Jing, HUANG Cai-hong, et al. The influence of motor elastic bogie-suspended parameters of high-speed vehicles on the dynamic performance of bogies[J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2018, 37(20): 95-100, 108. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZDCJ201820015.htm [11] HUANG Cai-hong, ZENG Jing. Suppression of the flexible carbody resonance due to bogie instability by using a DVA suspended on the bogie frame[J]. Vehicle System Dynamics, 2022, 60(9): 3051-3070. [12] 黄彩虹, 宋春元, 范军, 等. 电机弹性架悬高速转向架蛇行频率跳变现象分析[J]. 铁道学报, 2021, 43(10): 20-28. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDXB202110005.htmHUANG Cai-hong, SONG Chun-yuan, FAN Jun, et al. Analysis on hunting frequency jump phenomenon of high-speed bogies with elastic motor suspension[J]. Journal of the China Railway Society, 2021, 43(10): 20-28. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDXB202110005.htm [13] 李广, 张振先, 姚远, 等. 电机弹性架悬对高速列车的适应性研究[J]. 铁道科学与工程学报, 2023, 20(2): 441-452. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CSTD202302008.htmLI Guang, ZHANG Zhen-xian, YAO Yuan, et al. Research on the adaptability of motor elastic suspension to high-speed trains[J]. Journal of Railway Science and Engineering, 2023, 20(2): 441-452. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CSTD202302008.htm [14] 朱海燕, 黎洁, 尹必超, 等. 牵引电机悬挂参数对高速列车牵引传动部件振动特性的影响[J]. 交通运输工程学报, 2023, 23(1): 156-169. doi: 10.19818/j.cnki.1671-1637.2023.01.012ZHU Hai-yan, LI Jie, YIN Bi-chao, et al. Influence of suspension parameters of traction motor on vibration characteristics of traction drive components of high-speed train[J]. Journal of Traffic and Transportation Engineering, 2023, 23(1): 156-169. (in Chinese) doi: 10.19818/j.cnki.1671-1637.2023.01.012 [15] POLACH O. Characteristic parameters of nonlinear wheel/rail contactgeometry[J]. Vehicle System Dynamics, 2010, 48(S1): 19-36. [16] QI Ya-yun, DAI Huan-yun, SONG Chun-yuan, et al. Shaking analysis of high-speed train's carbody when cross lines[J]. Journal of Mechanical Science and Technology, 2019, 33(3): 1055-1064. [17] WEI Lai, ZENG Jing, CHI Mao-ru, et al. Carbody elastic vibrations of high-speed vehicles caused by bogie hunting instability[J]. Vehicle System Dynamics, 2017, 55(9): 1321-1342. [18] WANG Jian-bin, SONG Chun-yuan, WU Ping-bo, et al. Wheel reprofiling interval optimization based on dynamic behavior evolution for high speed trains[J]. Wear, 2016, 366/367: 316-324. [19] 杨震寰, 戴焕云, 石俊杰, 等. 磨耗后轮轨型面接触关系及线路适应性分析[J]. 铁道学报, 2021, 43(5): 37-46. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDXB202105007.htmYANG Zhen-huan, DAI Huan-yun, SHI Jun-jie, et al. Analysis of worn wheel-rail contact relationship and line adaptability[J]. Journal of the China Railway Society, 2021, 43(5): 37-46. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDXB202105007.htm [20] XU Kai, FENG Zheng, WU Hao, et al. Investigating the influence of rail grinding on stability, vibration, and ride comfort of high-speed EMUs using multi-body dynamics modelling [J]. Vehicle System Dynamics, 2019, 57(11): 1621-1642. [21] 周清跃, 田常海, 张银花, 等. CRH3型动车组构架横向失稳成因分析[J]. 中国铁道科学, 2014, 35(6): 105-110. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGTK201406017.htmZHOU Qing-yue, TIAN Chang-hai, ZHANG Yin-hua, et al. Cause analysis for the lateral instability of CRH3 EMU framework[J]. China Railway Science, 2014, 35(6): 105-110. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGTK201406017.htm [22] SUN Jian-feng, CHI Mao-ru, JIN Xue-song, et al. Experimental and numerical study on carbody hunting of electric locomotive induced by low wheel-rail contact conicity[J]. Vehicle System Dynamics, 2021, 59(2): 203-223. [23] MEI Tian-xiang, GOODALL R M. Wheelset control strategies for a two-axle railway vehicle[J]. Vehicle System Dynamics, 1999, 33(S1): 653-664. [24] MEI T X, LI H. Control design for the active stabilization of rail wheelsets[J]. Journal of Dynamic Systems, Measurement, and Control, 2008, 130(1): 011002. [25] DIANA G, BRUNI S, CHELI F, et al. Active control of the running behaviour of a railway vehicle: stability and curving performances[J]. Vehicle System Dynamics, 2002, 37(S1): 157-170. [26] BRAGHIN F, BRUNI S, RESTA F. Active yaw damper for the improvement of railway vehicle stability and curving performances: simulations and experimental results[J]. Vehicle System Dynamics, 2006, 44(11): 857-869. [27] YAO Yuan, ZHANG Xiao-xia, LIU Xu. The active control of the lateral movement of a motor suspended under a high-speed locomotive[J]. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part F: Journal of Rail and Rapid Transit, 2016, 230(6): 1509-1520. [28] ZHANG Xiao-xia, WU Guo-song, LI Guang, et al. Actuator optimal placement studies of high-speed power bogie for active hunting stability[J]. Vehicle System Dynamics, 2020, 58(1): 108-122. [29] FU Bin, GIOSSI R L, PERSSON R, et al. Active suspension in railway vehicles: a literature survey[J]. Railway Engineering Science, 2020, 28: 3-35. [30] 黄彩虹, 曾京, 魏来. 铁道车辆蛇行稳定性主动控制综述[J]. 交通运输工程学报, 2021, 21(1): 267-284. doi: 10.19818/j.cnki.1671-1637.2021.01.013HUANG Cai-hong, ZENG Jing, WEI Lai. Review on active control of hunting stability for railway vehicles[J]. Journal of Traffic and Transportation Engineering, 2021, 21(1): 267-284. (in Chinese) doi: 10.19818/j.cnki.1671-1637.2021.01.013 [31] WICKENS A H. The dynamic stability of railway vehicle wheelsets and bogies having profiled wheels[J]. International Journal of Solids and Structures, 1965, 1(3): 319-341. [32] WICKENS A H. Stability of high speed trains[J]. Physics in Technology, 1973, 4(1): 1-17. [33] AHMADIAN M, YANG Sao-pu. Hopf bifurcation and hunting behavior in a rail wheelset with flange contact[J]. Nonlinear Dynamics, 1998, 15(1): 15-30. [34] ZHANG Ting-ting, DAI Huan-yun. Loss of stability of a railway wheel-set, subcritical or supercritical[J]. Vehicle System Dynamics, 2017, 55(11): 1731-1747. [35] KALKER J J. Three-Dimensional Elastic Bodies in Rolling Contact[M]. Dordrecht: Kluwer Academic Publishers, 1990. [36] ZHOU D F, LI J, HANSEN C H. Application of least mean square algorithm to suppression of maglev track-induced self-excited vibration[J]. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 2011, 330(24): 5791-5811. [37] ZHOU Dan-feng, LI Jie, HANSEN C H. Suppression of maglev track-induced self-excited vibration using an adaptive cancellation algorithm[J]. Applied Mechanics and Materials, 2011, 44/45/46/47: 586-590. [38] WU S T, SHAO Y J. Adaptive vibration control using a virtual-vibration-absorber controller[J]. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 2007, 305(4/5): 891-903. -





 下载:
下载: