Analysis of subgrade deformation driving factors and climate resilience for highway in the Qinghai-Xizang Plateau permafrost region
-
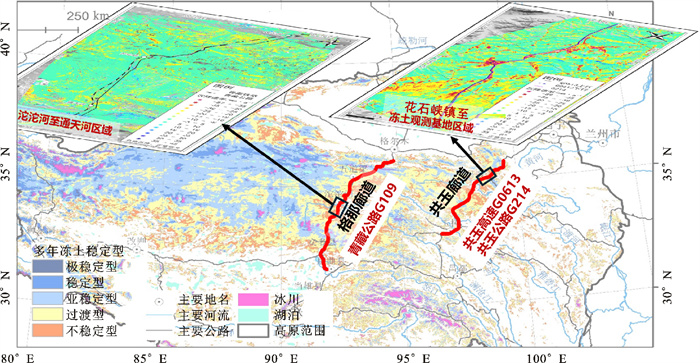
摘要: 为明确青藏高原多年冻土区在役公路路基变形的主要驱动因素及其对气候变化的适应能力,选取了穿越青藏高原多年冻土区的两大工程走廊——格尔木至那曲、共和至玉树的3条在役公路进行研究,分析了路基变形状况指标与气候环境参数、交通荷载差异、路基工程本体参数、路基工程所在场地参数的空间相关性;提出了青藏高原多年冻土区公路路基气候韧性的概念。分析结果表明:海拔高度与最大冻结深度、植被覆盖率与年累计降水量是影响路表国际平整度指数、跳车指标变化最主要的驱动因素,相关系数绝对值均超过0.4,明显区别于其他因素;季节冻土带无论年累计降水量高低,路面行驶质量指数(RQI)均保持良好以上;而多年冻土带的年累计降水量在220~370 mm区间时,RQI几乎全为差;多年冻土带的累计降水量达到370 mm以上时,多年冻土含冰量、地下水、土质类型和路侧积水侵蚀沿路线方向的跳跃性分布是其变形的主要驱动因素;此外,年降水量超过370 mm及路侧积水产生的热积累效应导致融区与多年冻土岛状交替发育,成为该区域无法明确强相关驱动因素的主要原因;路基总体随天然大地发生长周期沉降和季节性冻胀融沉,特殊结构路基可减缓形变速率,桩筏地基处理方式可有效终止沉降趋势;建议通过增强路面-路基-地基体系结构韧性及削弱气候环境对场地参数的不利影响等路径,提升多年冻土区公路路基的气候韧性,为该区域的公路工程维养改造提供理论指导和实践参考。Abstract: To identify the main driving factors of deformation for inservice highway subgrades in the permafrost region of the Qinghai-Xizang Plateau and their adaptability to climate change, three inservice highways crossing the two major engineering corridors — Golmud to Nagqu and Gonghe to Yushu in the permafrost region of the Qinghai-Xizang Plateau were selected. The spatial correlations between indicators of subgrade deformation and a range of factors, including climate environment parameters, traffic loading differences, inherent parameters of subgrade engineering, and parameters of the site where the subgrade engineering was located were examined. The concept of climate resilience for highway subgrades in the permafrost region of the Qinghai-Xizang Plateau was proposed. Analysis results show that elevation and maximum frozen depth, as well as vegetation coverage and annual cumulative precipitation, are the predominant driving factors influencing the variation of the international roughness index and bumpiness index, with absolute correlation coefficients exceeding 0.4, significantly distinguishing them from other factors. In the seasonal frozen zone, regardless of the annual cumulative precipitation, the road quality index (RQI) remains above good level. In the permafrost zone, when the annual cumulative precipitation is in the range of 220-370 mm, the RQI is mostly poor. However, when the annual cumulative precipitation exceeds 370 mm, the main driving factors of subgrade deformation are the ice content of permafrost, groundwater, soil type, and the jump-like distribution of roadside accumulated water erosion along the route. Furthermore, the heat accumulation effect caused by annual precipitation exceeding 370 mm and roadside water accumulation leads to the alternating development of thaw zones and permafrost islands, which is the main reason for the lack of clear strong correlation with the driving factors in this region. The subgrade overall follows the long-cycle subsidence and seasonal frost heave-thaw collapse of the natural terrain, and the use of subgrades with special structures can slow down the subsidence rate, while pile-raft foundation can effectively terminate the subsidence trend. It is recommended to enhance the structural resilience of the pavement-subgrade-foundation system and reduce the adverse impact of climate environment on site parameters to improve the climate resilience of highway subgrades in permafrost regions. This study provides theoretical guidance and practical reference for the maintenance and renovation of highway engineering in this region.
-
Key words:
- road engineering /
- climate resilience /
- correlation analysis /
- permafrost /
- subgrade deformation /
- driving factor
-
表 1 长基区域4个横切剖面不同结构类型路基的形变速率
Table 1. Deformation rates of different structural types of subgrades across four transverse profiles in the Changji area
剖面 冻土类型 冻土天然上限/m 土质类型 共玉高速上行 共玉高速下行 G214 路基类型 形变速率/ (mm·年-1) 路基类型 形变速率/ (mm·年-1) 路基类型 形变速率/ (mm·年-1) aa′ 富冰、含土冰层 2.5~3.0 粉质黏土、角砾 片块石路基 -22.9 片块石路基 -18.5 普通填土路基 -43.6 bb′ 富冰冻土 2.0~2.5 亚砂土、碎石土 片块石路基 -7.5 片块石路基 -12.0 普通填土路基 -13.4 cc′ 含土冰层 2.0~3.0 砾砂 热棒+片块石路基 -21.2 通风管路基 -21.8 普通填土路基 -25.1 dd′ 富冰冻土 2.0~3.0 粉土、砾碎石 片块石路基 -2.7 通风管路基 -7.0 普通填土路基 -12.9 -
[1] 陈德亮, 徐柏青, 姚檀栋, 等. 青藏高原环境变化科学评估: 过去、现在与未来[J]. 科学通报, 2015, 60(32): 3025-3035.CHEN De-liang, XU Bai-qing, YAO Tan-dong, et al. Assessment of past, present and future environmental changes on the Tibetan Plateau[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2015, 60(32): 3025-3035. [2] 中国气象局气候变化中心. 中国气候变化蓝皮书(2023)[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2023.CMA Climate Change Centre. Blue book on climate change in China (2023)[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2023. [3] 汪双杰. 多年冻土区公路路基尺度效应理论与方法[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2020.WANG Shuang-jie. Scale effect theory and method of road embankments in permafrost regions[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2020. [4] 包卫星, 刘亚伦, 毛雪松, 等. 高海拔多年冻土区砂石路面公路的路基温度场特征[J]. 交通运输工程学报, 2023, 23(4): 60-74. doi: 10.19818/j.cnki.1671-1637.2023.04.004 BAO Wei-xing, LIU Ya-lun, MAO Xue-song, et al. Characteristics of subgrade temperature field of gravel road in high altitude permafrost region[J]. Journal of Traffic and Transportation Engineering, 2023, 23(4): 60-74. doi: 10.19818/j.cnki.1671-1637.2023.04.004 [5] 权磊, 田波, 牛开民, 等. 青藏高原高等级道路路基路面温度变化特征[J]. 交通运输工程学报, 2017, 17(2): 21-30. https://transport.chd.edu.cn/article/id/201702003QUAN Lei, TIAN Bo, NIU Kai-min, et al. Temperature variation properties of pavements and subgrades for high-grade roads on Qinghai-Tibet Plateau[J]. Journal of Traffic and Transportation Engineering, 2017, 17(2): 21-30. https://transport.chd.edu.cn/article/id/201702003 [6] 马巍, 穆彦虎, 李国玉, 等. 多年冻土区铁路路基热状况对工程扰动及气候变化的响应[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 2013, 43(3): 478-489.MA Wei, MU Yan-hu, LI Guo-yu, et al. Response of thermal state of railway subgrade in permafrost region to engineering disturbance and climate change[J]. Scientia Sinica: Terrae, 2013, 43(3): 478-489. [7] RAN Y H, CHENG G D, DONG Y H, et al. Permafrost degradation increases risk and large future costs of infrastructure on the Third Pole[J]. Communications Earth & Environment, 2022, 3(1): 238. [8] HOLLING C S. Resilience and stability of ecological systems[J]. Annual Review of Ecology and Systematics, 1973(4): 1-23. [9] 黄晓明, 赵润民. 道路交通基础设施韧性研究现状及展望[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(6): 1529-1549.HUANG Xiao-ming, ZHAO Run-min. Status and prospects of highway transportation infrastructure resilience research[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(6): 1529-1549. [10] 冉有华, 李新, 程国栋, 等. 2005~2015年青藏高原多年冻土稳定性制图[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 2021, 51(2): 183-200.RAN You-hua, LI Xin, CHENG Guo-dong, et al. Mapping the permafrost stability on the Tibetan Plateau for 2005-2015[J]. Scientia Sinica: Terrae, 2021, 51(2): 183-200. [11] 青藏公路科研组. 高原多年冻土地区有关路基稳定的几个问题[R]. 北京: 青藏公路科研组, 1978.Qinghai-Tibet Highway Research Group. Several issues related to the stabilization of highway subgrade in plateau permafrost region[R]. Beijing: Qinghai-Tibet Highway Research Group, 1978. [12] 窦明健, 胡长顺, 多吉罗布, 等. 青藏公路路面病害成因分析[J]. 冰川冻土, 2003(4): 439-444.DOU Ming-jian, HU Chang-shun, DUOJI Luo-bu, et al. Analysis on surface troubles of the Qinghai-Tibet Highway[J]. Journal of Glaciology and Geocryology, 2003(4): 439-444. [13] 吴青柏, 张中琼, 刘戈. 青藏高原气候转暖与冻土工程的关系[J]. 工程地质学报, 2021, 29(2): 342-352.WU Qing-bai, ZHANG Zhong-qiong, LIU Ge. Relationships between climate warming and engineering stability of permafrost on Qinghai-Tibet Plateau[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2021, 29(2): 342-352. [14] CHAI M T, MU Y H, ZHANG J M, et al. Characteristics of asphalt pavement damage in degrading permafrost regions: Case study of the Qinghai-Tibet Highway[J]. Journal of Cold Regions Engineering, 2018, 32(2): 05018003. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)CR.1943-5495.0000165 [15] CHAI M T, LI G Y, MA W, et al. Damage characteristics of the Qinghai-Tibet Highway in permafrost regions based on UAV imagery[J]. International Journal of Pavement Engineering, 2023, 24(2): 2038381. doi: 10.1080/10298436.2022.2038381 [16] XU L X, YANG D W, WU T H, et al. An ecosystem services zoning framework for the permafrost regions of China[J]. Advances in Climate Change Research, 2019, 10(2): 92-98. doi: 10.1016/j.accre.2019.06.007 [17] SUMMERS J K, HARWELL L C, BUCK K D, et al. Development of a climate resilience screening index (CRSI): An assessment of resilience to acute meteorological events and selected natural hazards[R]. Washington DC: US Environmental Protection Agency, 2017. [18] SCHEER J, TOMASKOVICOVA S, INGEMAN-NIELSEN T. Thaw settlement susceptibility mapping for roads on permafrost-towards climate-resilient and cost-efficient infrastructure in the Arctic[J]. Cold Regions Science and Technology, 2024, 220(104136): 1-21. [19] 吕松涛, 赵霈, 鲁巍巍, 等. 面向长寿命的既有高速公路沥青路面延寿设计综述[J]. 交通运输工程学报, 2024, 24(2): 20-49. doi: 10.19818/j.cnki.1671-1637.2024.02.002LYU Song-tao, ZHAO Pei, LU Wei-wei, et al. Review on long-life-oriented life extension design of existing expressway asphalt pavement[J]. Journal of Traffic and Transportation Engineering, 2024, 24(2): 20-49. doi: 10.19818/j.cnki.1671-1637.2024.02.002 [20] 胡静, 唐跃, 张家康, 等. 水位抬升对高铁路基动力响应与长期沉降的影响[J]. 交通运输工程学报, 2023, 23(4): 75-91. doi: 10.19818/j.cnki.1671-1637.2023.04.005HU Jing, TANG Yue, ZHANG Jia-kang, et al. Influences of water level rise on dynamic responses and long-term settlement of high-speed railway subgrade[J]. Journal of Traffic and Transportation Engineering, 2023, 23(4): 75-91. doi: 10.19818/j.cnki.1671-1637.2023.04.005 [21] 张明礼, 周志雄, 周凤玺, 等. 降雨对多年冻土区公路路基内部水热影响试验[J]. 长安大学学报(自然科学版), 2024, 44(4): 38-47.ZHANG Ming-li, ZHOU Zhi-xiong, ZHOU Feng-xi, et al. Influence of rainfall on hydrothermal process within highway subgrade in permafrost regions[J]. Journal of Chang'an University (Natural Science Edition), 2024, 44(4): 38-47. -





 下载:
下载: