Obstacle avoidance path planning of intelligent electric vehicles in winding road scene
Article Text (Baidu Translation)
-
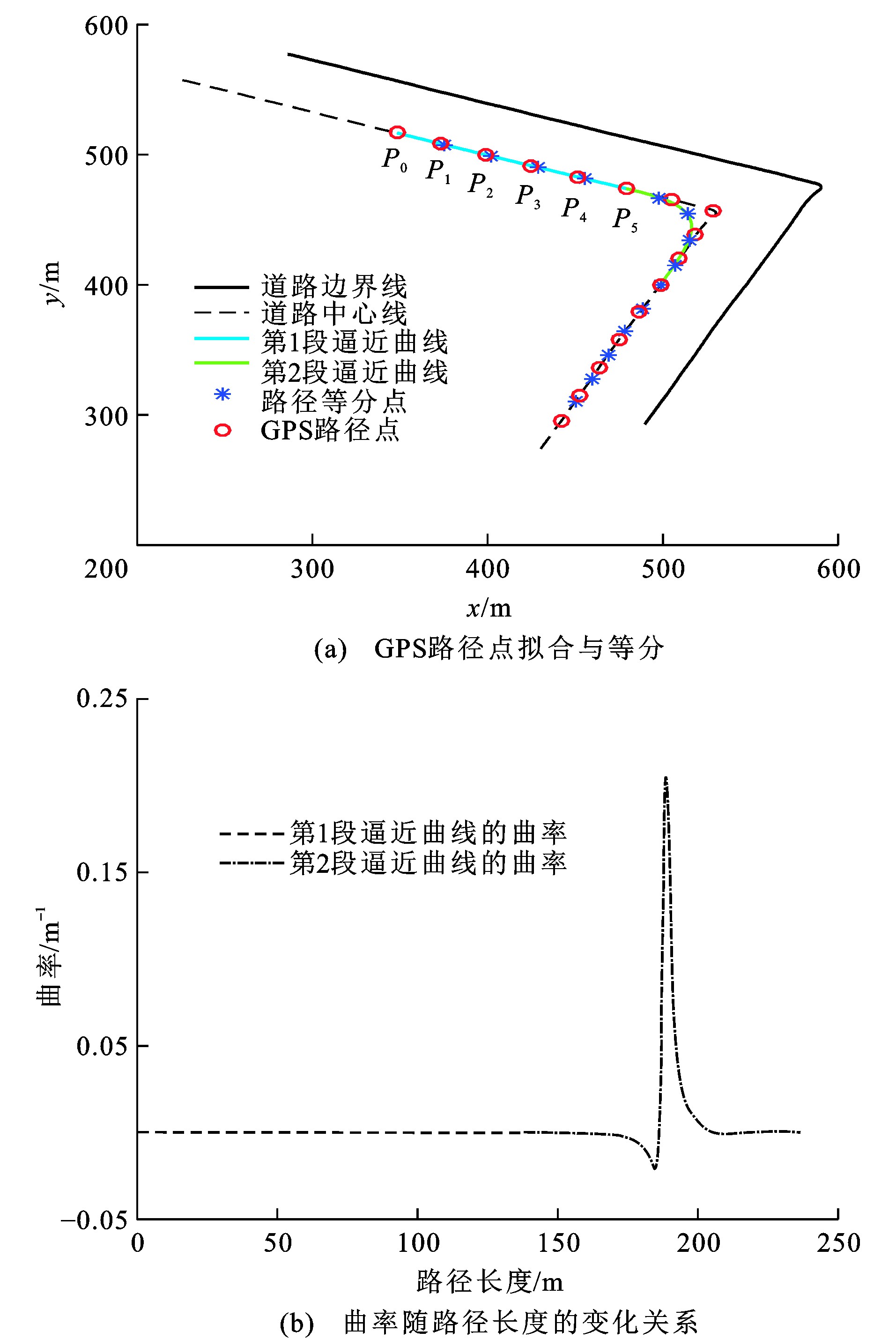
摘要: 为研究智能电动车在弯曲道路场景下进行避障规划的有效性, 提出了一种将笛卡尔坐标系转换为曲线坐标系的方法, 利用5次贝塞尔曲线对弯曲道路场景中的车道线进行逼近得到参考路径, 通过对参考路径进行弧长参数化, 以弧长为横坐标, 横向偏移为纵坐标的方法建立曲线坐标系, 根据车辆和子目标点在曲线坐标系中的位置关系, 采用3次多项式实时生成候选路径, 利用序列二次规划算法对候选路径进行优化; 为验证所提算法的有效性, 以某智能电动车为平台, 利用单目相机、64线激光雷达、工控机等设备搭建试验车, 通过Apollo平台对车辆在弯曲道路场景中的避障算法进行在线仿真, 在园区实车试验中对避障算法进行了GPS位置误差和航向角累计误差分析。研究结果表明: 在曲线坐标系中进行车辆弯曲道路场景下的避障路径规划, 能有效地描述规划路径曲率半径、车辆中心位置偏移车道线距离等信息, 容易确定自身车辆的可行驶区域、前方障碍物位置信息, 从而生成最优路径; 在园区场景的避障过程中, GPS位置误差发生在初始点、转弯点以及避障点, 最大误差为0.15 m, 航向角累计误差为12°, 突然增大的弯道位置误差主要由车辆姿态瞬时改变及障碍物匹配过程引起, 但是误差都能够很好地控制在一定范围之内, 利用曲线坐标系解决弯曲道路场景中的避障路径规划是可行的。Abstract: In order to study the reliability of obstacle avoidance planning for intelligent electric vehicles in the winding road scene, a method of converting the Cartesian coordinate system into the curvilinear coordinate system was proposed. The quintic Bézier curve was used to approximate the lane line in the winding road scene to obtain the reference path. Through the arc-length parameterization of reference path, a curvilinear coordinate system was established by using the arc-length as abscissa and the lateral offset as ordinate. According to the position of the vehicle and the sub-target points in the curvilinear coordinate system, the candidate paths were generated by the cubic polynomial in real time, and the candidate paths were optimized by using the sequence quadratic planning method. In order to verify the reliability of the proposed algorithm, an electric vehicle was used as a platform to build a test car with monocular cameras, 64-line laser radar, industrial control computers and other equipments. The online simulation of vehicle obstacle avoidance algorithm in the winding road scene was implemented based on Apollo platform. During the real vehicle experiment in the zone, the GPS position error and heading angle cumulative error of the obstacle avoidance algorithm were analyzed. Research result shows that the obstacle avoidance path planning of vehicle in the winding road scene can effectively describe the information of path curvature radius, the offset distance of vehicle center from the lane line, etc, and it is easy to determine the driving area of the vehicle and the obstacle position information ahead, so as to generate the optimal path. During the obstacle avoidance in the zone, the GPS position error occurs at the initial point, turning point and obstacle avoidance point, the maximum error is 0.15 m, and the heading angle cumulative error is 12°. The sudden increase of curve position error is mainly caused by the instantaneous change of vehicle posture and the matching process of obstacles, but the error can be well controlled within a certain range. So it is feasible to solve the obstacle avoidance path planning in the winding road scene by using the curvilinear coordinate system.
-
表 1 试验参数
Table 1. Test parameters
车型尺寸(长、宽、高)/mm 4 680、1 720、1 530 最小制动距离/m 16.6 轴距/mm 2 700 方向盘转角/(°) -540~540 车速阈值/(km·h-1) 60 安全距离阈值/m 0.8 加速度阈值/(m·s-2) 8 最小转弯半径/m 6 道路宽度/m 3.75 雷达感知窗口(长、宽)/m 20×10 -
[1] 李克强, 戴一凡, 李升波, 等. 智能网联汽车(ICV)技术的发展现状及趋势[J]. 汽车安全与节能学报, 2017, 8(1): 1-14. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-8484.2017.01.001LI Ke-qiang, DAI Yi-fan, LI Sheng-bo, et al. State-of-the-art and technical trends of intelligent and connected vehicles[J]. Journal of Automotive Safety and Energy, 2017, 8(1): 1-14. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-8484.2017.01.001 [2] LI Xiao-hui, SUN Zhen-ping, CAO Dong-pu, et al. Real-time trajectory planning for autonomous urban driving: framework, algorithms and verifications[J]. IEEE/ASME Transactions on Mechatronics, 2016, 21(2): 740-753. doi: 10.1109/TMECH.2015.2493980 [3] 周伟, 李军. 自动驾驶车辆避障路径规划研究综述[J]. 汽车工程师, 2018(5): 55-58. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-6546.2018.05.015ZHOU Wei, LI Jun. Research on obstacle avoidance path planning of automatic driving vehicle[J]. Auto Engineer, 2018(5): 55-58. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-6546.2018.05.015 [4] AYAWLI B B K, CHELLALI R, APPIAH A Y, et al. An overview of nature-inspired, conventional, and hybrid methods of autonomous vehicle path planning[J]. Journal of Advanced Transportation, https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/8269698. [5] 朱曼曼, 杜煜, 张永华, 等. 基于模糊逻辑的智能车局部路径规划[J]. 北京联合大学学报, 2016, 30(4): 29-32. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BJLH201604005.htmZHU Man-man, DU Yu, ZHANG Yong-hua, et al. Local path planning of smart car based on fuzzy logic method[J]. Journal of Beijing Union University, 2016, 30(4): 29-32. (in Chinese). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BJLH201604005.htm [6] 《中国公路学报》编辑部. 中国汽车工程学术研究综述·2017[J]. 中国公路学报, 2017, 30(6): 1-197.Editorial Department of China Journal of Highway and Transport. Review on China's automotive engineering research progress: 2017[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2017, 30(6): 1-197. (in Chinese). [7] 余卓平, 李奕姗, 熊璐. 无人车运动规划算法综述[J]. 同济大学学报(自然科学版), 2017, 45(8): 1150-1159. doi: 10.11908/j.issn.0253-374x.2017.08.008YU Zhuo-ping, LI Yi-shan, XIONG Lu. A review of the motion planning problem of autonomous vehicle[J]. Journal of Tongji University (Natural Science), 2017, 45(8): 1150-1159. (in Chinese). doi: 10.11908/j.issn.0253-374x.2017.08.008 [8] EIHOSENY M, THARWAT A, HASSANIEN A E. Bezier curve based path planning in a dynamic field using modified genetic algorithm[J]. Journal of Computational Science, 2018, 25(5): 339-350. [9] GONZALEZ D, PEREZ J, MILANESV, et al. A review of motion planning techniques for automated vehicles[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2017, 17(4): 1135-1145. [10] 陈成, 何玉庆, 卜春光, 等. 基于四阶贝塞尔曲线的无人车可行轨迹规划[J]. 自动化学报, 2015, 41(3): 486-496. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MOTO201503004.htmCHEN Cheng, HE Yu-qing, BU Chun-guang, et al. Feasible trajectory generation for autonomous vehicles based on quartic Bezier curve[J]. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2015, 41(3): 486-496. (in Chinese). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MOTO201503004.htm [11] 宋晓琳, 潘鲁彬, 曹昊天. 基于改进智能水滴算法的汽车避障局部路径规划[J]. 汽车工程, 2016, 38(2): 185-191, 228. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-680X.2016.02.009SONG Xiao-lin, PAN Lu-bin, CAO Hao-tian. Local path planning for vehicle obstacle avoidance based on improved intelligent water drops algorithm[J]. Automotive Engineering, 2016, 38(2): 185-191, 228. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-680X.2016.02.009 [12] 宋晓琳, 周南, 黄正瑜, 等. 改进RRT在汽车避障局部路径规划中的应用[J]. 湖南大学学报(自然科学版), 2017, 44(4): 30-37. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HNDX201704005.htmSONG Xiao-lin, ZHOU Nan, HUANG Zheng-yu, et al. An improved RRT algorithm of local path planning for vehicle collision avoidance[J]. Journal of Hunan University (Natural Sciences), 2017, 44(4): 30-37. (in Chinese). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HNDX201704005.htm [13] 安林芳, 陈涛, 成艾国, 等. 基于人工势场算法的智能车辆路径规划仿真[J]. 汽车工程, 2017, 39(12): 1451-1456. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QCGC201712015.htmAN Lin-fang, CHEN Tao, CHENG Ai-guo, et al. A simulation on the path planning of intelligent vehicles based on artificial potential field algorithm[J]. Automotive Engineering, 2017, 39(12): 1451-1456. (in Chinese). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QCGC201712015.htm [14] 王畅, 付锐, 张琼. 换道决策中的车辆速度估计模型[J]. 交通运输工程学报, 2015, 15(6): 83-91. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1637.2015.06.011WANG Chang, FU Rui, ZHANG Qiong. Speed estimation model during lane-changing decision[J]. Journal of Traffic and Transportation Engineering, 2015, 15(6): 83-91. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1637.2015.06.011 [15] 李红, 王文军, 李克强. 基于B样条理论的平行泊车路径规划[J]. 中国公路学报, 2016, 29(9): 143-151. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7372.2016.09.019LI Hong, WANG Wen-jun, LI Ke-qiang. Path planning for parallel parking based on B spline theory[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2016, 29(9): 143-151. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7372.2016.09.019 [16] 徐美华, 张凯欣, 蒋周龙. 一种实时车道线偏离预警系统算法设计和实现[J]. 交通运输工程学报, 2016, 16(3): 149-158. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1637.2016.03.018XU Mei-hua, ZHANG Kai-xin, JIANG Zhou-long. Algorithm design and implementation for a real-time lane departure pre-warning system[J]. Journal of Traffic and Transportation Engineering, 2016, 16(3): 149-158. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1637.2016.03.018 [17] SHENG Peng-cheng, MA Jin-gang, WANG Da-peng, et al. Intelligent trajectory planning model for electric vehicle in unknown environment[J]. Journal of Intelligent and Fuzzy Systems, 2019, 37: 397-407. doi: 10.3233/JIFS-179095 [18] 郭蓬, 吴学易, 戎辉, 等. 基于代价函数的无人驾驶汽车局部路径规划算法[J]. 中国公路学报, 2019, 32(6): 79-85. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGGL201906009.htmGUO Peng, WU Xue-yi, RONG Hui, et al. Local path planning of driverless cars based on cost function[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2019, 32(6): 79-85. (in Chinese). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGGL201906009.htm [19] LI Xiao-hui, SUN Zhen-ping, CAO Dong-pu, et al. Development of a new integrated local trajectory planning and tracking control framework for autonomous ground vehicles[J]. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 2017, 87: 118-137. doi: 10.1016/j.ymssp.2015.10.021 [20] JIANG Yun-cheng, JIN Xiao-feng, XIONG Yan-fei, et al. A dynamic motion planning framework for autonomous driving in urban environments[J]. Electrical Engineering and Systems Science, 2019(9): 1-7. [21] CHU K, LEE M, SUNWOO M. Local path planning for off-road autonomous driving with avoidance of static obstacles[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2012, 13(4): 1599-1616. doi: 10.1109/TITS.2012.2198214 [22] BARFOOT T D, CLARK C M. Motion planning for formations of mobile robots[J]. Robotics and Autonomous Systems, 2004, 46(2): 65-78. [23] WALTON D J, MEEKD S, AlI J M. Planar G2 transition curves composed of cubic Bezier spiral segments[J]. Journal of Computational and Applied Mathematics, 2003, 157(2): 453-476. doi: 10.1016/S0377-0427(03)00435-7 [24] SCHLECHTRIEMEN J, WABERSICH K P, KUHMERT K D. Wiggling through complex traffic: planning trajectories constrained by predictions[C]∥IEEE. 2016 IEEE Intelligent Vehicles Symposium. New York: IEEE, 2006: 1-8. [25] YANG K, SUKKARIEH S. An analytical continuous-curvature path-smoothing algorithm[J]. IEEE Transactions on Robotics, 2010, 26(3): 561-568. doi: 10.1109/TRO.2010.2042990 [26] SHU Si-hui, LIN Zi-zhi, DING Yun. B-spline curve approximation with nearly arc-length parameterization[J]. Applied Mechanics and Materials, 2014, 513-517: 3372-3376. [27] 许小勇, 钟太勇. 三次样条插值函数的构造与Matlab实现[J]. 兵工自动化, 2006, 25(11): 76-78. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BGZD200611035.htmXU Xiao-yong, ZHONG Tai-yong. Construction and realization of cubic spline interpolation function[J]. Ordnance Industry Automation, 2006, 25(11): 76-78. (in Chinese). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BGZD200611035.htm [28] GUENTER B, PARENT R. Computing the arc length of parametric curves[J]. IEEE Computer Graphics and Applications, 1990, 10(3): 72-78. [29] 盛鹏程, 曾小松, 罗新闻, 等. 基于贝叶斯概率估计的智能电动车动态目标避障算法[J]. 中国公路学报, 2019, 32(6): 96-104. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGGL201906011.htmSHENG Peng-cheng, ZENG Xiao-song, LUO Xin-wen, et al. Multi-objective dynamic obstacle avoidance algorithm of intelligent electric vehicles based on Bayesian theory[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2019, 32(6): 96-104. (in Chinese). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGGL201906011.htm [30] GILL P E, KUNGURTSEV V, ROBINSON D P. A stabilized SQP method: superlinear convergence[J]. Mathematical Programming, 2017, 163(1/2): 369-410. -





 下载:
下载: